The franhoff Solar System Research Institute has again successfully improved the efficiency of single-chip three junction solar cells made of silicon and III-V semiconductor materials, raising the world record to 34.1%, and the solar cell efficiency record of III-V semiconductor layer directly deposited on silicon to 24.3%.
The eg of GaAs material is 1.43ev. In the above high efficiency range, it is theoretically estimated that the efficiency of GaAs single junction solar cell can reach 27%,Since the 1980s, GaAs solar cell technology has experienced several development stages from LPE to MOCVD, from homogeneous epitaxy to heterogeneous epitaxy, and from single junction to multi junction laminated structure. Its development speed has been accelerated and its efficiency has been continuously improved. At present, the maximum efficiency of the laboratory has reached 50% (data from IBM), and the industrial production conversion rate can reach more than 30%.
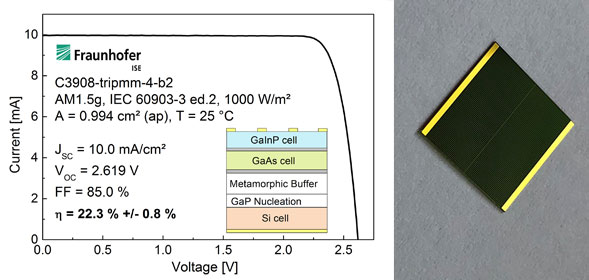
Compared with single junction solar cells, multi junction solar cells are the source of hope for the further development of silicon solar cells in this field because they can significantly improve the efficiency. Using a combination of various absorbing materials, the energy of multi junction cells using the solar spectrum is significantly better than that of traditional silicon solar cells. Scientists believe that they can achieve an efficiency value of 36%, which greatly exceeds the physical limit of 29.4% of pure silicon solar cells.
High photoelectric conversion efficiency means more power generation per unit surface area, thus saving solar cells and module materials - an important aspect of photovoltaic sustainability.
A few microns thick III-V semiconductor thin layer is deposited on the silicon solar cell. Different layers absorb light from different spectral ranges: gallium phosphide absorbs visible light in the range of 300-660 nm, aluminum gallium arsenide corresponds to near-infrared light in the range of 600-840 nm, and silicon layer can absorb long wavelength light in the range of 800-1200 nm. Compared with single junction silicon cells, multi junction photovoltaic cells can make the best use of sunlight and improve efficiency.