A thin film gallium arsenide (GaAs) solar cell is used to replace the silicon solar cell and gallium arsenide crystal base solar cell widely used at present, so as to solve the defects of low photoelectric conversion efficiency, poor resistance to cosmic environmental conditions, heavy weight and high cost of gallium arsenide crystal base solar cell. Based on the advantages of light proportion of silicon material, high mechanical strength, high photoelectric conversion efficiency of gallium arsenide material and good resistance to cosmic environmental conditions, Japan Institute of electrical communication adopts metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) to generate a layer of gallium arsenide film on silicon crystal to form thin-film gallium arsenide solar cells.
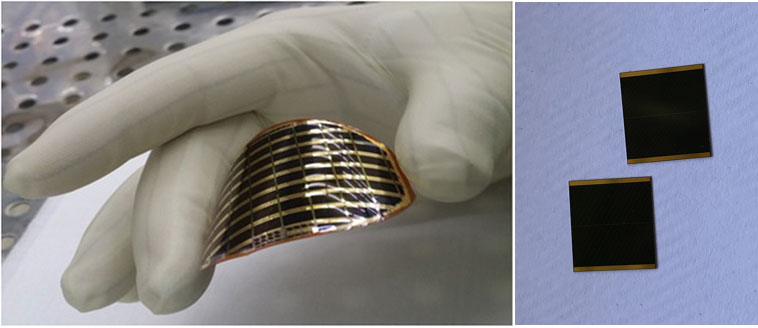
High efficiency GaAs solar cells are the main energy source of space satellites and other aircraft. With the development of space technology, the requirements for the conversion efficiency of solar cells are higher and higher. In addition, it is also necessary to continuously reduce the weight of solar cells and improve the specific energy. Flexible thin film GaAs solar cells have the characteristics of high efficiency, high weight specific power, thin thickness and flexibility. Their application prospects have attracted more and more attention from major research institutions at home and abroad.Thin film solar cells are new photovoltaic devices to alleviate the energy crisis. Thin film solar cells can be made of low-cost ceramics, graphite, metal sheets and other different materials as substrates. It takes only a few to form a thin film thickness that can generate voltage μ m. At present, the conversion efficiency can be up to 13%. Thin film solar cells are not only planar, but also flexible. They can be made into non planar structures. They have a wide range of applications. They can be combined with buildings or become a part of buildings. They are widely used.