The effect of beta radiation on the performance of GaAs solar cells with a series of structures was studied. The solar cells with shallow and deep junctions fabricated on the first wafers are irradiated by 1-mev electrons, and therefore the energy density is as high as 1 × 1015 e-/cm2. The degradation of gaas mj cell performance caused by radiation is studied experimentally and theoretically by using model simulation, and a group of coherent minority carrier lifetime damage constants are derived.
The performance degradation of gaas mj cells mainly depends on the junction depth and thickness of the active layer, and therefore the material damage isn't sensitive to the gaas mj cell structure and manufacturing steps. Modeling studies show that additionally to reducing the carrier lifetime, beta radiation also will strongly affect the standard of the heterogeneous interface, which is never mentioned within the literature.
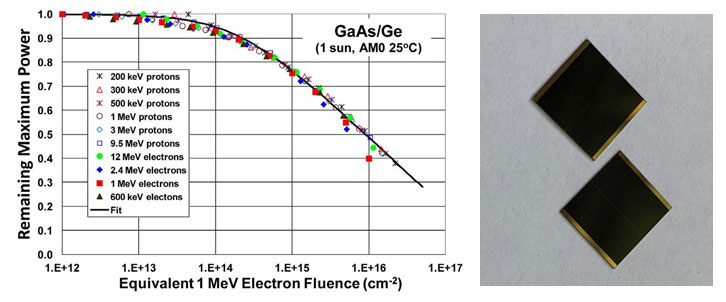
The results show that the linear increase of the electron fluence of the recombination velocity on the surface of the heterogeneous interface before and after the concentrated photovoltaic cell accurately describes the degradation of the spectral response and dark current characteristics during irradiation. The shallow junction solar cells fabricated as thin film devices have rock bottom sensitivity to beta radiation , and therefore the efficiency at the top of life is 82% of that at the start of life.
With the rapid development of space technology and therefore the complexity of space tasks, the demand for space solar cells is increasing. Space solar cells face more severe challenges than ever: higher conversion efficiency and better radiation resistance. because the main power source of spacecraft, III-V multi junction solar cells became the most focus of space applications thanks to their high efficiency and super radiation resistance. within the multi junction concentrated photovoltaic cell structure, the key to get high crystal quality and improve gaas mj cell efficiency is to satisfy the lattice matching and band gap matching conditions.
In recent years, new materials and structures of high efficiency multi junction solar cells are emerging, which have the characteristics of low cost, lightweight, flexible, high power to mass ratio then on. additionally to efficiency and other performance, radiation resistance is another unique standard of space solar cells, therefore the radiation effect and radiation damage mechanism of gaas mj cells are widely studied within the past decades. This review briefly summarizes the research progress of III-V multi junction solar cells in recent years. differing types of concentrated photovoltaic cell structures, research results and radiation effects of those concentrated photovoltaic cell structures under different irradiation conditions are introduced. Two main radiation damage assessment models of solar cells, equivalent flux method and displacement damage dose method, are introduced.