The concentrator photovoltaics CPV module has a backplane on which a 1mm² or smaller concentrator photovoltaics cell array is provided. The backplane interconnection network is additionally provided on the backplane. The backplane interconnection network is employed to attach the concentrator photovoltaic cell array together. Provide front panel separated from backplane. The front panel includes a primary lens array facing the photovoltaic cell array above it. The front panel are often configured to supply quite 1000 times the lens to the solar battery for light aggregation. so as to realize the sunshine concentration from the 1000 times lens to the unit, the most lens are often configured as a flat converging lens with a lens drooping but about 4 mm. A secondary optical element array can also be provided, which extends between the first lens array and therefore the concentrator photovoltaic cell array.
Inspired by sunflower, scientists have developed a sunflower shaped solar concentrator photovoltaics. They say the concentrator photovoltaic will revolutionize the solar field. The new solar concentrator uses several mirrors to focus sunlight on the converter chip. Experts say the solar concentrator could be used to power remote areas.
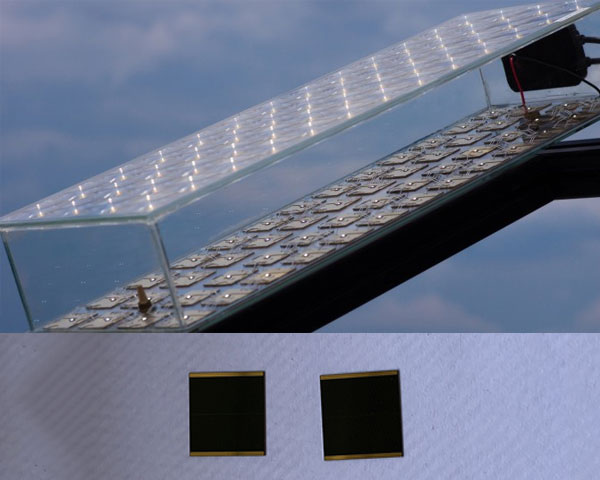
Scientists hope the project will develop affordable optoelectronic systems that can collect 80% of the sunlight and convert it into electricity. The system can be built in any area that lacks sustainable energy, potable water and cold air at a cost of one-third that of a similar system. The prototype of this system uses a huge parabolic cylindrical reflector and consists of several small mirrors. They're connected to a tracking system. The tracking system determines the optimal angle according to the position of the sun. Parabolic reflector reflects sunlight to several microchannel liquid cooling receivers with concentrator photovoltaic chips. The size of each chip is 1 × 1 cm, if calculated according to the sunshine time of 8 hours per day, the average electricity can be generated from 200 to 250 watts. According to news this week, the Swiss Commission on technology and innovation awarded a three-year $2.4 million research fund to IBM research institutes, solar energy, scientists from the Federal Institute of technology in Zurich, Switzerland, and the University of technology and economic application sciences of Kur and the Buchs interstate College of technology. They will be responsible for the research and development of the project. This project is called economic high concentrated solar photovoltaic power generation and photothermal system (hereinafter referred to as HCPVT).
The whole receiver of hcpvt system has hundreds of concentrator photovoltaic chips, which can provide 25 kilowatt power. The photoelectric chip is installed in the microstructure layer, which is responsible for delivering liquid coolant to a position only tens of microns away from the chip. The role of coolant is to absorb heat and the efficiency is 10 times higher than that of the current system. Bruno Mitchell of IBM Research Institute said: we plan to use three-node photocell on microchannel cooling module, which can directly convert more than 30% of the collected sunlight into electricity, and allow the recovery efficiency of waste heat to reach more than 50%.