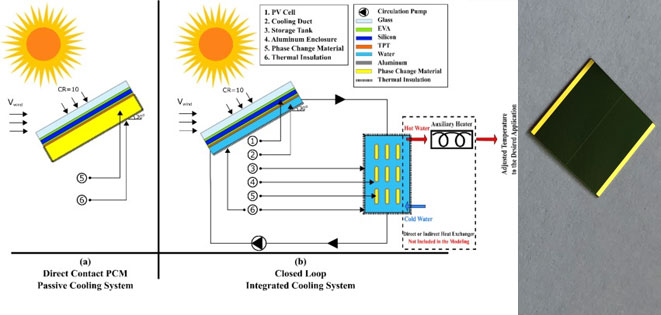
At present, the conversion efficiency of indium phosphide / gallium indium arsenic / germanium triple junction Concentrated pv cell has been reported to be 41.1%. However, even with such high conversion efficiency, about 60% of the energy is still converted into heat. If the Concentrated pv cell is not cooled, too high temperature will reduce the conversion efficiency of the Concentrated pv cell, and long-term high temperature will cause irreversible damage to the cell.
Traditional concentrated pv cell cooling mode
Air cooling: natural convection is adopted. A copper or aluminum heat dissipation base plate can be added on the back of the Concentrated pv cell, or fins can be added to increase the heat exchange effect. Natural cooling has the advantages of convenient installation and low cost, but the cooling effect is limited.
Traditional concentrated pv cell cooling mode
Water cooling: according to the table below, the heat transfer property of water is much better than that of air.
| Traditional Concentrated pv cell cooling mode | Process convective heat transfer coefficient(W/m2K) | |
| process | Air | 1~10 |
| Natural flow | Water | 200 ~ 1000 |
| Air | 20 ~ 100 | |
| Forced counter flow | Water | 1000 ~ 15000 |
| Concentrated pv cell type | Condenser multiple | cooling mode |
| Single Concentrated pv cell | 1-1000 | air-cooled, heat pipe |
| Linear condenser | <25 | water cooled, heat pipe |
| ≥25 | water cooling, liquid immersion | |
| Concentrated pv cell array | <150 | microchannel, heat pipe |
| ≥150 | microchannel, jet impact, liquid immersion |