In CPV system, sunlight is concentrated on a small area for photoelectric conversion, so there are high requirements for the conversion efficiency and high temperature resistance of photovoltaic cells. Therefore, the III-V group element compound multi junction battery which can still ensure high conversion efficiency at high temperature (above 200 ℃) is an ideal choice for battery modules in CPV system.Multi junction cells originated from the non condensing photovoltaic conversion system used in man-made satellites. After improvement, they can withstand up to 8A / cm2 current density at 500 times high power condensing. Under concentrating conditions, compared with traditional silicon battery, multi junction light made of III-V group element compounds.
Temperature also affects the performance of solar cells. When the temperature increases, the open circuit voltage decreases linearly. Solar cells of different materials have their own operating temperature range. For a solar cell, the optimal load required to obtain the maximum output power is also different at different temperatures.
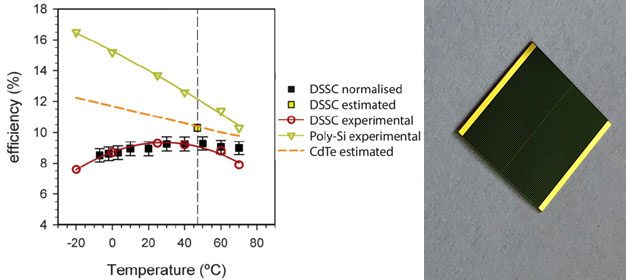
The relationship between temperature and short-circuit current is that the higher the temperature, the greater the short-circuit current. However, it should be noted that the increasing trend of short-circuit current is less than the decreasing trend of open circuit voltage in the first article above, that is, the curve between temperature and short-circuit current is a straight line with a slightly positive slope, In the testing of solar module certification, this is called testing the current temperature coefficient of solar cells
The open circuit voltage of single solar cell decreases with the increase of product degree, and the voltage temperature coefficient is - (210 ~ 212) MV / ℃. That is, the open circuit voltage of single solar cell decreases by 210 ~ 212mv every 1 ℃ increase in temperature; Short circuit current of solar cell varies with temperature.
Increase with the increase of; The peak power of solar cells decreases with the increase of temperature (directly affecting the efficiency), that is, every time the temperature increases.At 1 ℃, the peak power loss rate of solar cells is 0135 ~ 0145%. For example, silicon solar cells working at 20 ℃,The output power is 20% higher than that at 70 ℃.